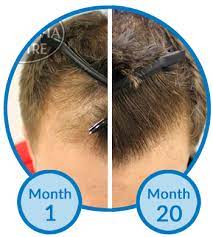
Receding hairlines are most prevalent among men, though women may experience them too. Luckily, there are several treatments available that may slow or reverse this condition.
Causes
Healthy hair follicles on your scalp produce new strands to replace those shed, giving you a full head of hair and an established fuller-looking hairline. But when these follicles become damaged or stop making new growth strands, you could experience loss and receding hairlines.
Receding hairline typically indicates pattern baldness, the most prevalent form of hair loss among men and women. hair loss typically begins near either the temples or crown area before progressing forward in front of the scalp area – with women often experiencing a widow’s peak due to this process.
Alongside genetics and getting older, hairline recession can also be caused by certain medications, stress levels, diet choices, and lifestyle decisions like wearing your hair tightly back or using harsh products. One of the leading causes for women is known as “traction alopecia,” wherein their hair is repeatedly pulled back for styling purposes.
Diagnosis
Although your hairline may be receding, it’s essential to remember that not all scalp thinning is equal. One way of telling whether or not it lessens as opposed to becoming finer and thinner over time is looking back through old photos of yourself and taking note of the direction your hairline is moving and how different it appears from before. It can help guide whether consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist might be beneficial in treatment options.
Their physician will ask those experiencing receding hairlines about a family history of baldness and any symptoms they are experiencing, which may include hair thinning. A scalp biopsy could also be recommended to examine the more closely, and blood work could also help identify conditions that could contribute to hair loss (e.g., thyroid disease), which will assist the doctor in providing suitable solutions – this might include minoxidil, finasteride medications or hair transplant surgery if appropriate.
Treatment
Various treatments are available for those experiencing receding hairlines, including prescription medicines such as finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine). Both can help slow hair loss in some instances.
Hair restoration surgery may also provide a solution. This procedure involves transplanting healthy strands from the back of the head into areas where follicles have stopped producing, potentially reversing receding hairlines in some instances.
Other types of hair loss can be treated through various hairstyles, such as fringe or bangs that cover the forehead and hide receding widow’s peaks. Avoiding tight-pulling styles that pull on hair directly can also help prevent traction alopecia – which occurs from too much stress on hair follicles, causing hair loss.
Prevention
Some treatments available may help stop receding hairlines if caught early enough, including minoxidil (Rogaine for women), which promotes new growth while thickening thinned-out hair follicles. These medications are available over-the-counter and have been proven successful by various studies.
Reducing breakage by keeping hair at a healthy length and not over-styling it are also ways to prevent split ends and give fuller locks. Eating foods rich in antioxidants like blueberries, spinach, and kidney beans may also aid healthy hair.
Men with male baldness can use fringes or bangs cut into their hair to disguise a receding line and conceal other signs of thinning or receding hair. Other options for hiding receding lines, like hair restoration surgery, which transplants scalp follicles into areas where growth has stopped occurring to promote new growth, may also provide relief. This procedure is offered to men and women suffering from hereditary hair loss, such as male pattern baldness.

