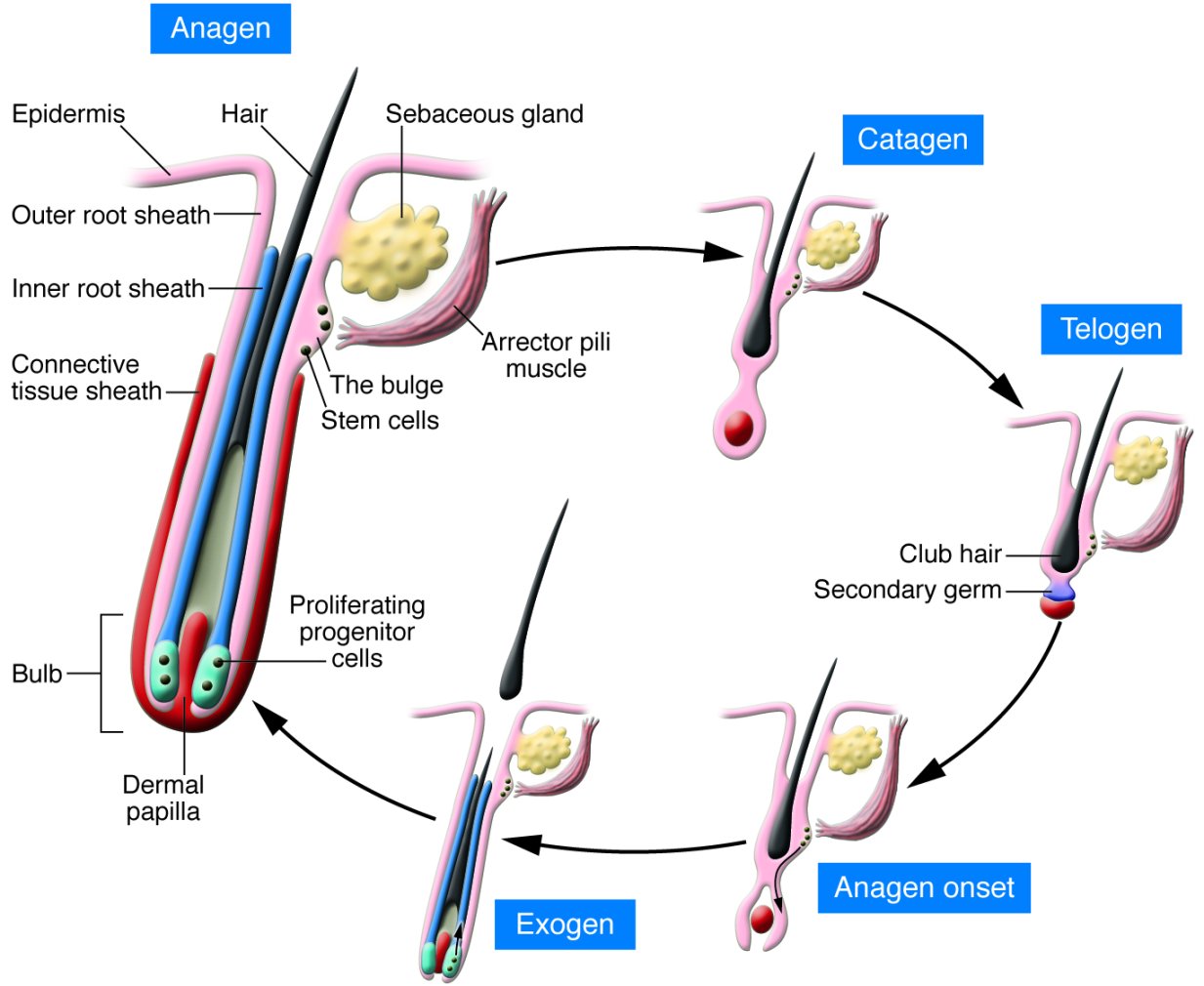
Anagen Phase
The anagen phase is the longest and most active stage of hair growth. During this phase, the cells in the hair bulb divide rapidly, promoting growth. It typically lasts two to seven years, and about 80% to 90% of our hair is in this stage at any given time. However, eyelashes and pubic hair have shorter anagen phases than scalp hair. The hair follicle enters the catagen phase at the end of this phase.
Catagen Phase
The catagen phase is the shortest in the hair growth cycle, typically lasting about one week. During this phase, the follicles contract and move upward, detach from their nutrient source, and slow down in growth. The size of the follicles decreases, and they become club hair. This club hair will eventually be shed during the telogen phase.
Telogen Phase
The telogen phase, also known as the resting stage, is the final phase of the hair growth cycle. It lasts approximately three months. During this phase, club hairs rest without access to a blood supply or the cells that produce new hair follicles. You may notice natural or brush-induced hair shedding during this time.
Exogen Phase
The exogen phase is a more recent addition to the hair growth cycle. In this phase, old club fibers are released from the follicle and shed physically.
Understanding the different phases of the hair growth cycle is essential to comprehend why hair grows and falls out. Factors like nutritional deficiencies, stress, and lifestyle choices can disrupt this cycle. However, natural botanical remedies can help combat hair loss and prevent premature balding by influencing the ratio between the anagen and telogen phases.
Treatments like Low-Level Laser Therapy can also stimulate hair follicles to remain in the anagen phase longer, which is crucial for hair growth. It is worth noting that disrupting the cycle, whether due to nutritional deficiencies or diseases, can lead to noticeable symptoms such as thinning hair or even hair loss.

