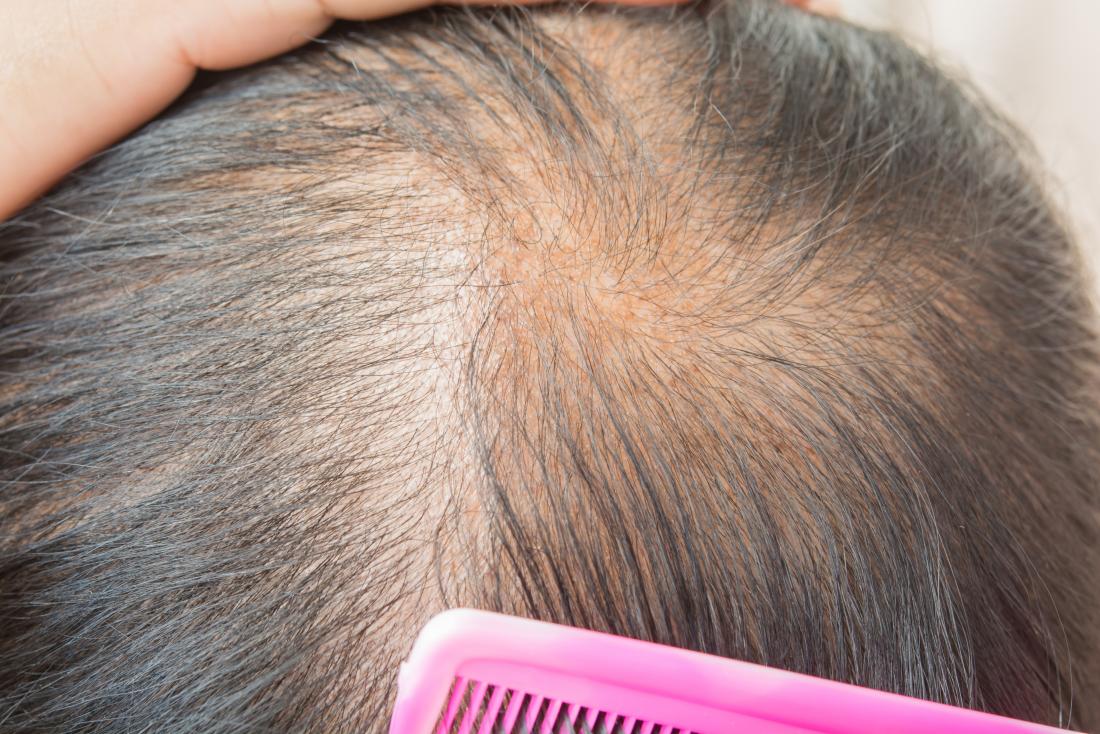
Hair comprises cells called follicles, which form distinct areas on the scalp, face, and torso. Sparse hair refers to a decrease in the density of these follicles, resulting in limited water retention within the hair cuticles.
Diseases: Genetic hair Disorders
Genetic hair disorders often cause sparse and fragile hair. One common disorder is hypohidrosis ectodermal dysplasia (HED). People with HED may experience pattern baldness during puberty. Their scalp hair becomes thin, patchy, wiry, brittle, and lighter in color. Eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair also become sparse or absent.
HED and Clouston Syndrome
Missense mutations in the GJB6 gene can cause HED. Clouston syndrome, another condition, also leads to HED through modifications in the same gene. Both conditions result in damaged hair cuticles, as seen under light microscopy. It is important to note that individuals with HED may also lack sweating.
Menkes Syndrome
Menkes syndrome is an X-linked recessive condition caused by mutations in the ATP7A gene, which encodes copper-transporting ATPase. This leads to imbalanced copper levels and systemic dysfunctions affecting skin, eyes, bones, muscles, and hair follicles. One noticeable symptom is sparse hair with a steel wool appearance, often accompanied by hypopigmented eyebrows and eyelashes.

